
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing
1. Spark - Introduction
| Year | Version | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Spark_launched | Designed to solve the limitations of the MapReduce computing model. |
| 2014 | Spark 1.0 | Introduced the Spark SQL module for structured data processing. |
| 2016 | Spark 2.0 | Unified DataFrame and Dataset APIs. |
| 2020 | Spark 3.0 | Introduced Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) and Dynamic Partition Pruning. |
| 2023 | Spark 3.5.0 | SQL Functionality Enhancements; Introduction of the IDENTIFIER clause (SPARK-43205); Adding SQL functions to Scala, Python, and R APIs (SPARK-43907) |
| 2024 | Spark 3.5.1 | (Details to be announced by the official release) |
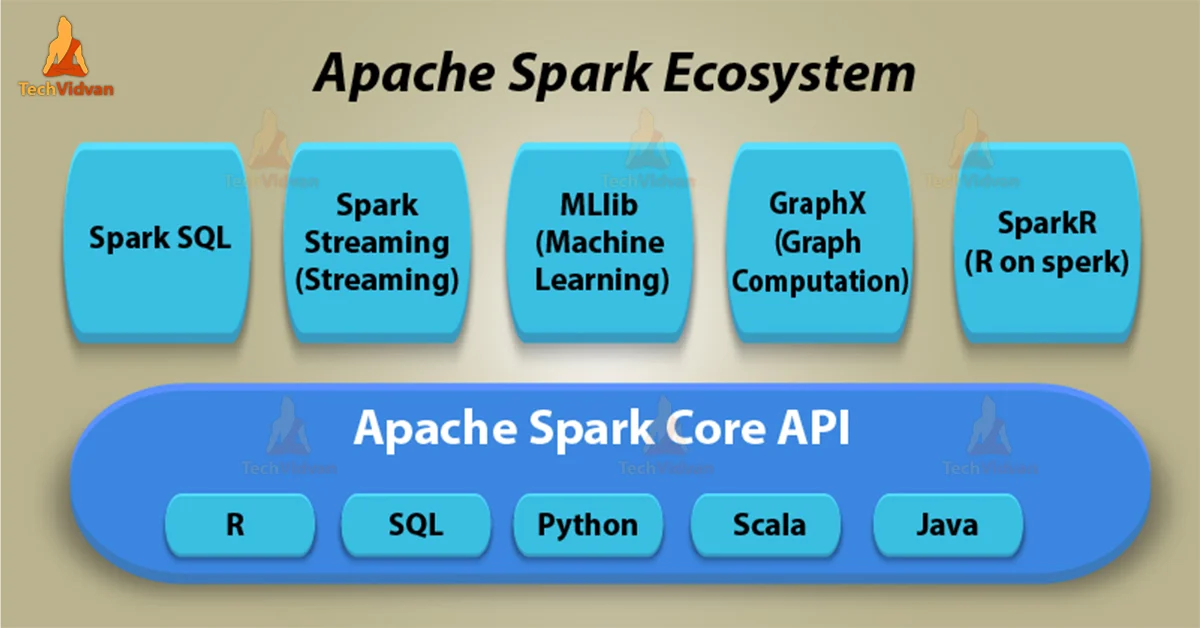
2. Spark - Ecosystem
3. Spark vs Hadoop
Spark is an alternative to MapReduce and is compatible with distributed storage layers such as HDFS and Hive.
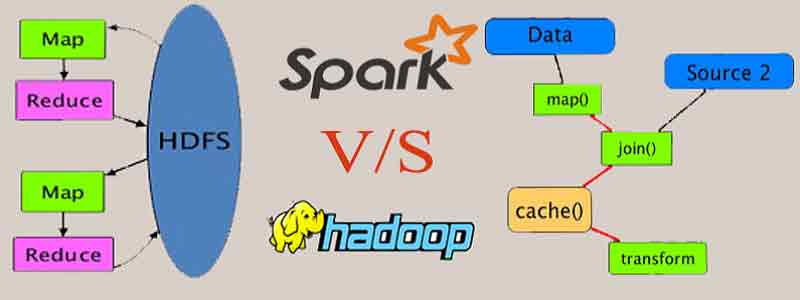
Spark advantages as follows:
| Aspect & Question | Spark | Hadoop MapReduce |
|---|---|---|
| How does it handle data processing? | Stores intermediate data in memory, reducing I/O overhead. | Writes to disk, increasing I/O overhead. |
| What is its fault tolerance mechanism? | Uses Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) for fault tolerance. | Relies on data replication across the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). |
4. Spark - Quick Start
Spark is a computing framework that mainly uses HDFS as the persistence layer.
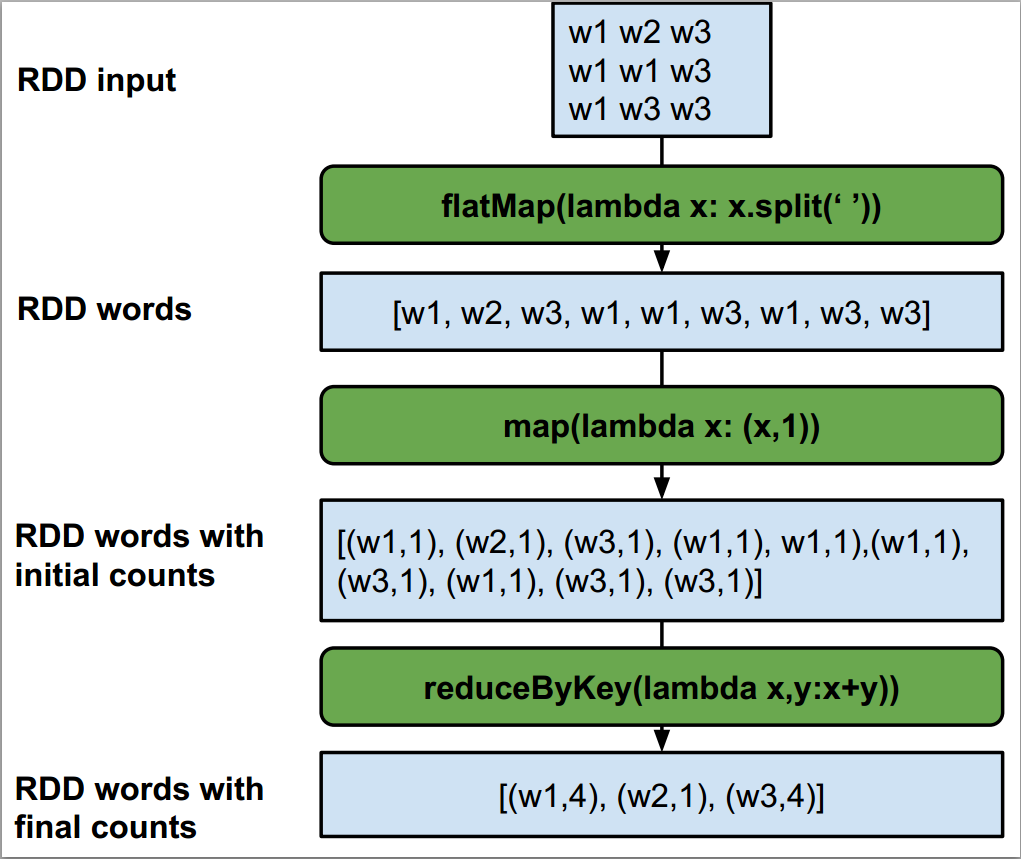
4.1 Spark-Shell
1 | from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext |
reduceByKey: Merge values with the same key (such as summation, maximum value, etc.). This step reduces the amount of data before Shuffle.
Advantages: For large data sets, this method is more efficient because it reduces the amount of data during network transmission.
4.2 DataFrame API
1 | from pyspark.sql import SparkSession |
In SQL, there is no direct reduceByKey
SQL, as a declarative query language, describes “What you want” rather than “How to do it”.
SQL作为一种声明式查询语言,它描述的是“What you want”而不是“How to do it”。GROUP BY combined with aggregate functions provides a universal way to group and aggregate data without specifying the exact steps to process the data. This conceptually differs from more operational functions like
reduceByKeyin Spark or other programming frameworks.
GROUP BY配合聚合函数提供了一种通用的方式来对数据进行分组和聚合,而不需要指定处理数据的具体步骤。这与Spark或其他编程框架中reduceByKey这类更具操作性的函数在概念上存在差异。In SQL, data aggregation and grouping are achieved by using GROUP BY along with aggregate functions, which is the standard method for handling such tasks in SQL.
在SQL中,用GROUP BY加上聚合函数来实现数据的聚合和分组,这是SQL处理这类任务的标准方法。
4.3 SparkSQL
uses DataFrame for data processing with SparkSQL
1 | from pyspark.sql import SparkSession |
Within the code, the DataFrame API to read a text file and then register it as a temporary view to perform data processing and querying through SQL statements.
- Syntax and readability: The DataFrame API prefers programmatic processing, while Spark SQL provides a declarative query method, which may be more friendly to users familiar with SQL.
- Temporary view: In Spark SQL implementation, DataFrame needs to be registered as a temporary view to execute SQL queries, while the DataFrame API operates directly on the data.
quick-start : https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/quick-start.html
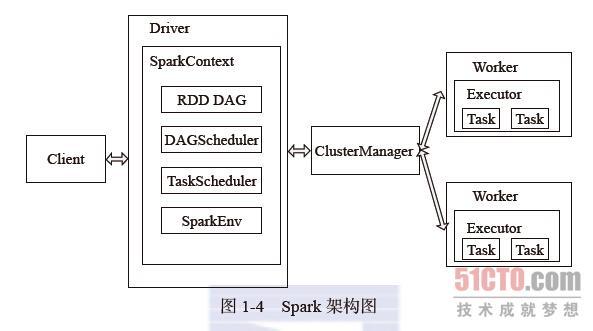
5. Spark - Architecture
The Spark architecture adopts the Master-Slave model common in distributed computing.
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Master | Corresponds to the node in the cluster that contains the Master process, acting as the controller of the cluster. 对应集群中的含有Master进程的节点, 集群的控制器 |
| Slave | Worker Nodes in the cluster 集群中含有Worker进程的节点 |
| Client | Acts as the client on the user’s behalf, responsible for submitting applications. 作为用户的客户端负责提交应用 |
| Driver | Runs the main() function of the application and creates a SparkContext. Responsible for the scheduling of jobs, i.e., the distribution of tasks. 运行Application的main()函数并创建SparkContext。负责作业的调度,即Task任务的分发 |
| Worker | Manages compute nodes and creates Executors, responsible for launching Executors or Drivers. Receives commands from the master node and reports status. |
| Executor | A component on the worker node that executes tasks, responsible for task execution, and uses a thread pool to run tasks. |
| Cluster Manager | In Standalone mode, acts as the Master, controlling the entire cluster and monitoring workers. Standalone 模式中为 Master, 控制整个集群, 监控Worker |
| SparkContext | The context of the entire application, controlling the lifecycle of the application. <整个应用的上下文, 控制App的生命周期> |
| RDD | The basic computation unit in Spark, a collection of RDDs can form a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) for execution. Spark的基本计算单元,一组RDD可形成执行的 DAG |
| Num | Spark App Process |
|---|---|
| 1. | Client submits the application. / 客户端提交应用。 |
| 2. | Master finds a Worker to start the Driver. / Master找到一个Worker启动Driver。 |
| 3. | The Driver requests resources from the Master or resource-manager, then converts the application into an RDD Graph. / Driver向Master或资源管理器申请资源,之后将应用转化为RDD图。 |
| 4. | DAGScheduler converts RDD-Graph into directed acyclic graph (DAG) of Stages, submits to TaskScheduler. DAGScheduler将RDD图转化为Stage的有向无环图,提交给TaskScheduler。 |
| 5. | TaskScheduler submits tasks to Executors for execution. TaskScheduler提交任务给Executor执行。 |
| 6. | During task execution, other components together to ensure the smooth execution of the entire application. 在任务执行的过程中,其他组件协同工作,确保整个应用顺利执行。 |
During the execution phase, the Driver serializes Tasks along with any files and jars they depend on and sends them to the corresponding Worker machines. Executors then process tasks on their assigned data partitions.
在执行阶段,Driver会将Task和Task所依赖的文件及jar序列化后传递给对应的Worker机器,Executor随后对分配给它们的数据分区的任务进行处理。
6. Summary
Introduced spark three ways to write wordcount program
In large company production environments, storing data in Hive and querying it directly with Spark SQL is a common practice. This approach primarily leverages the DataFrame API.






Checking if Disqus is accessible...